Welcome back to Issue 30 of Healthy Innovations! 👋
Today we're exploring AlphaGenome, the new AI tool from Google DeepMind that's transforming our understanding of the human genome. This powerful system predicts with unprecedented accuracy how single DNA variants affect the biological processes regulating our genes.
Having manually sequenced DNA with radioactive labeling in the 1990s (and hating it!), I find this week's topic particularly exciting.
The healthcare implications are extraordinary. AlphaGenome could fundamentally change personalized medicine by enhancing genetic diagnostics and treatment optimization. Beyond individual care, it promises to accelerate biomedical research by revealing how genetic variations function across populations, potentially uncovering new therapeutic targets and treatment approaches.
Ready to explore this genetic revolution? Let's dive in!
The genome challenge
The human genome is a vast, incredibly detailed instruction manual written in a language of DNA, composed of four "letters": A, C, G, and T. The sequence of these letters contains all the information needed to build and operate a human being.
Only about 2% of the human genome codes for proteins - this is what Google DeepMind’s other AI tool, AlphaFold excels at predicting. The remaining 98%, called non-coding regions, are crucial for orchestrating gene activity and contain many variants linked to diseases. Scientists call this the "dark matter" of the genome.
Here's the challenge: small variations in these DNA sequences can have significant consequences, influencing everything from disease susceptibility to medication response. Deciphering exactly how these tiny changes affect biological processes at a molecular level has been one of biology's greatest mysteries.
Traditional approaches have faced a fundamental trade-off: they could either analyze very long stretches of DNA with limited detail or provide high-resolution insights for only very short segments. This limitation has made it difficult to get a comprehensive picture of how changes in our DNA affect cellular function.
Enter AlphaGenome: A new kind of genome reader
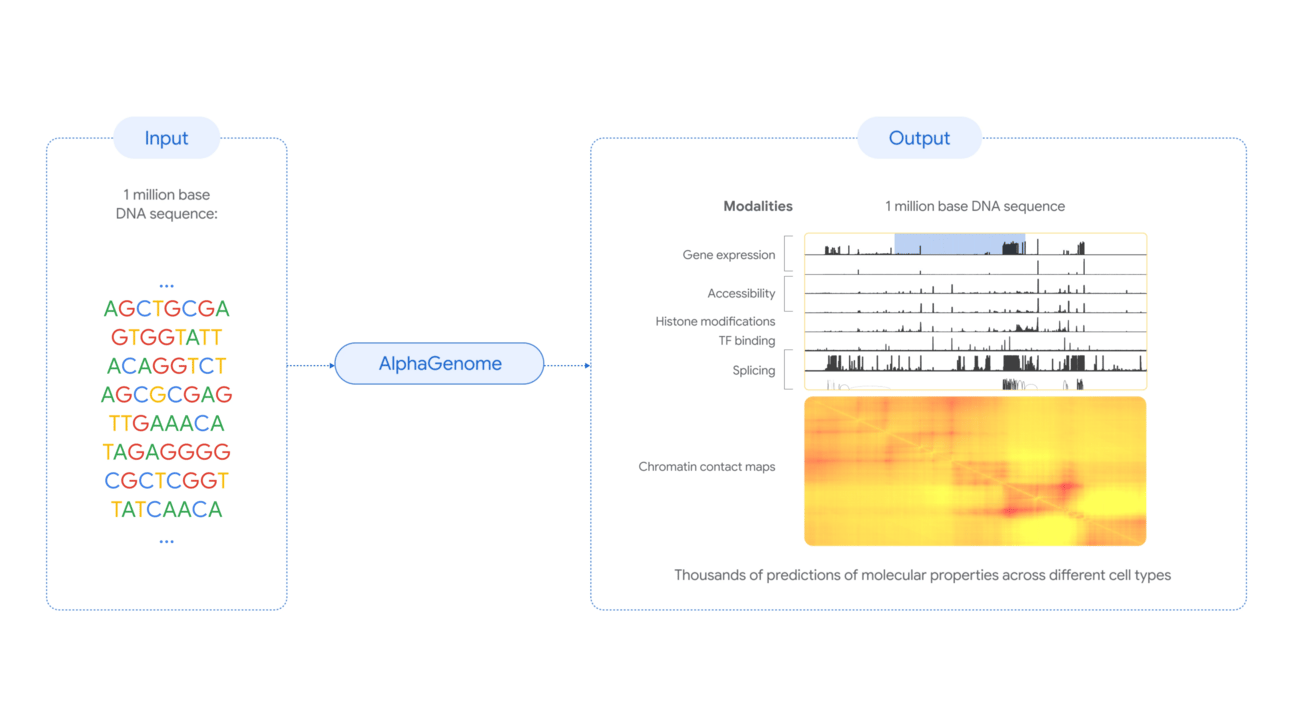
Newly-launched AlphaGenome overcomes these limitations by offering a more comprehensive and accurate way to predict how changes in human DNA sequences affect biological processes that regulate genes.
Think of it as an advanced "reader" of the genome's instruction manual that can understand not just individual words, but entire chapters, and predict the consequences of even subtle edits.
Here's what makes AlphaGenome so impressive:
Long-range vision with precision: Unlike previous models, AlphaGenome can process up to 1 million DNA letters while still making predictions at the resolution of individual letters
Comprehensive analysis: It simultaneously predicts thousands of molecular properties, including where genes start and end, how much RNA is produced, and where proteins bind to DNA
Rapid variant assessment: The tool can assess the impact of a genetic variant on multiple molecular properties in less than a second
Advanced splice modeling: For the first time, it can directly model the precise location and amount of RNA produced at splice junctions - critical for understanding many rare genetic diseases.
Real-world applications
AlphaGenome's capabilities open up exciting new avenues for research and healthcare:
Disease understanding: By accurately predicting the molecular consequences of genetic disruptions, AlphaGenome could help researchers pinpoint the underlying causes of diseases with greater precision. This is particularly promising for rare genetic disorders, where a single variant can have profound effects
Synthetic biology: The tool's predictive power could guide the design of synthetic DNA sequences with specific desired functions - imagine designing DNA that only activates a gene in nerve cells but not in muscle cells
Drug discovery: By providing a complete picture of how genetic variants influence gene regulation, AlphaGenome could aid in identifying individuals who might respond better to certain treatments, moving us closer to personalized medicine
Fundamental research: AlphaGenome can accelerate our basic understanding of the human genome, helping map crucial functional elements and their roles in cellular function.
The technology behind the breakthrough
AlphaGenome was trained on vast amounts of data from major research initiatives including ENCODE, GTEX, 4D Nucleome, and FANTOM5. These projects have experimentally measured molecular properties of DNA across hundreds of human and mouse cell types and tissues.
The model has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of genomic prediction benchmarks, outperforming or matching the best available specialized models in the vast majority of evaluations.
Current limitations
While AlphaGenome represents a significant leap forward, it has limitations:
Distant regulatory elements: Accurately capturing the influence of very distant regulatory elements remains challenging
Cell specificity: Improving accuracy across all cellular contexts is an ongoing priority
Personal genome prediction: The model focuses on individual genetic variants rather than entire personal genomes
Complex traits: While it excels at predicting molecular outcomes, it doesn't provide the full picture of how variations lead to complex diseases involving broader biological processes.
🔮 Looking ahead
AlphaGenome marks a foundational step toward unraveling the remaining mysteries of the genome and translating that knowledge into improved health outcomes. Google DeepMind is committed to continuously improving the tool and addressing its current limitations through ongoing research.
The availability of AlphaGenome via an API for non-commercial research significantly enables broader access and collaborative discovery. By fostering collaboration across academia, industry, and government, this tool has the potential to drive exciting new discoveries in genomics and healthcare.
We're witnessing the emergence of AI as a powerful ally in understanding the complex cellular processes encoded in our DNA - and that understanding could ultimately benefit everyone through better treatments, earlier disease detection, and more personalized medicine.
Innovation highlights
🖨️ 3D diabetes breakthrough. Researchers have successfully 3D-printed functional human insulin-producing islets that maintain strong responses for three weeks - a major leap toward curing Type I diabetes. Using a novel bioink derived from human pancreatic tissue, the team achieved 90% cell survival after 21 days, with printed islets releasing insulin in response to glucose levels just like natural pancreatic cells. Unlike traditional islet transplants that require infusion into the liver, these 3D-printed structures can be implanted just under the skin through a minimally invasive procedure, making them easier to monitor and remove if needed.
🧬 DIY human genome. Scientists are taking "build-your-own" to the next level by creating human genomes from scratch. This controversial project, called the Synthetic Human Genome Project, goes beyond editing existing DNA - researchers want to synthesize entire human genetic blueprints using AI assistance. While experts are excited about potential medical breakthroughs, they're also raising eyebrows about the ethical implications of essentially writing humanity's instruction manual from the ground up.
💉 Cholesterol kill switch. Scientists have identified an enzyme called IDO1 that acts as a molecular "off switch" for the body's cholesterol-processing machinery during inflammation. By blocking this enzyme, macrophages regain their ability to absorb cholesterol effectively, potentially preventing heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and other inflammation-linked conditions before they start. The team also discovered that targeting a second enzyme, nitric oxide synthase, alongside IDO1 could create a powerful two-pronged therapy - offering hope for millions affected by chronic inflammation and opening doors to next-generation treatments that tackle disease at its molecular roots.
Company to watch
🎓 Kolabtree is democratizing scientific expertise by creating the world's largest marketplace connecting organizations with freelance PhD-qualified researchers. This London-based platform gives businesses instant access to over 10,000 experts from 175+ countries across 2,500+ scientific disciplines, from data analysis and medical writing to experimental design and regulatory consulting. Their standout feature is the secure, flexible model that allows companies to tap into expertise from institutions like NASA, MIT, and Harvard without long-term hiring commitments.
As healthcare and biotech innovation accelerates, Kolabtree's on-demand science model is transforming how organizations access specialized knowledge - enabling startups to compete with industry giants and established companies to rapidly expand their research capabilities. Kolabtree exemplifies the growing gig economy in science, making world-class expertise available at the speed of innovation.

Weird and wonderful
👃🏼 Tiny sinus terminators. Scientists have developed micro-robots thinner than human hair that can be injected up your nose to fight sinus infections! These magnetic copper warriors are guided by external fields to infected areas, then activated by light to heat up and literally melt through bacterial defenses. Successfully tested in rabbits and pigs, these microscopic terminators could reduce antibiotic use and tackle stubborn infections in sinuses, bladders, and lungs within the next decade. “Nano-robots’ behaviour is often simpler and more targeted than many drugs and they could effectively complement a wide range of therapies.”
Thank you for reading the Healthy Innovations newsletter!
Keep an eye out for next week’s issue, where I will highlight the healthcare innovations you need to know about.
Have a great week,
Alison ✨
P.S. Join over 500 healthcare leaders who get these insights delivered straight to their inbox! Healthy Innovations is read weekly by executives from AstraZeneca, GSK, Vertex, Roche, and leading healthcare startups, agencies, and investors. Subscribe now to stay ahead of industry trends!