Welcome back to Issue 31 of Healthy Innovations! 👋
This week, I'm exploring the use of exosomes in medicine. Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles naturally released by cells that act as messengers facilitating cellular communication. Scientists once dismissed these lipid packages as cellular debris. Today, they're being re-addressed and stuffed with siRNA (silencing RNA), CRISPR editors, and enzymes to treat diseases that antibodies and viral vectors struggle to reach.
The field is gaining momentum, with early research suggesting that exosome-based therapies may promote faster healing, modulate inflammation, and support tissue repair in ways that could complement or enhance conventional treatments. Exosomes have also become a buzzword in the beauty industry, where they're being investigated for their potential to support healthier, more youthful-looking skin and hair.
So let's dive into the nano world of exosomes!
📬 All past issues of the newsletter are available here, covering everything from brain-computer interfaces to biotech startup valuations.
Your body is constantly engaged in self-repair. Behind the scenes, cells coordinate complex healing processes, dispatching microscopic messengers to injured tissues. Among the most powerful of these messengers are exosomes - tiny, cell-derived vesicles that deliver regenerative instructions exactly where they're needed.
Once overlooked as biological debris, exosomes are now at the forefront of regenerative medicine, transforming approaches to chronic wounds, cardiac injury, neurodegeneration, and more. Exosomes have also become a buzzword in the beauty industry, where they are being investigated for their potential to support healthier, more youthful-looking skin and hair, but the true innovation is unfolding in hospitals and research labs worldwide.
Venture investors have also taken note, with around $500 million funneled into exosome companies over the past year, reflecting growing confidence that these natural messengers could outshine synthetic alternatives in tissue repair.
🦠 Exosome therapy is a specific type of extracellular vesicle (EV) therapy. While all exosomes are EVs, not all EVs are exosomes - EV therapy may use a broader range of vesicles, including exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies.
Exosomes: The body’s natural repair signal
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (30-150 nanometers) secreted by nearly all cells. Unlike synthetic drug carriers, exosomes evolved to coordinate communication and healing across tissues.
In regenerative medicine, they function as:
Tissue repair orchestrators, delivering growth factors, RNAs, and proteins that drive regeneration
Inflammation regulators, modulating immune responses to create optimal healing environments
Stem cell guides, directing stem cell migration, differentiation, and integration at injury sites
Matrix remodelers, influencing the rebuilding of tissue architecture
Their biocompatibility, stability, and natural targeting ability make them uniquely suited for regenerative therapies, overcoming limitations that plague traditional approaches.
Changing the face of regenerative medicine
The exosome revolution is transforming regenerative medicine across multiple therapeutic areas, with dozens of clinical trials now underway to harness these natural couriers for healing damaged tissues.
Wound healing: Exosome therapies, especially those from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), are showing promise in accelerating closure of chronic wounds by stimulating angiogenesis, collagen production, and cell migration.
Cardiac repair: Following heart attacks, exosomes are being explored to promote heart muscle recovery and reduce scar formation. Exosomes can be directly delivered to the site of injury and contribute to improved cardiac function by stimulating angiogenesis, reducing apoptosis, and promoting tissue repair.
Musculoskeletal repair: Exosomes enhance bone and cartilage regeneration, offering hope for osteoarthritis and fracture healing where conventional treatments often fall short.
Neural regeneration: Exosomes’ ability to cross the blood-brain barrier is driving innovation in repairing neural tissues damaged by stroke, trauma, or degenerative disease.
Why exosomes outshine traditional regenerative methods
Unlike stem cell therapies that can be invasive and expensive or growth factor injections that degrade rapidly, exosomes bring unique advantages.
They offer targeted delivery, homing naturally to sites of tissue injury without the need for invasive procedures. Because they are derived from a patient’s own cells or well-matched donors, they provide reduced immunogenicity and lower the risk of immune complications.
Exosomes also ensure greater stability, shielding regenerative molecules from degradation and extending bioactivity. Most importantly, they deliver a synergistic mix of regenerative signals rather than relying on single-agent interventions.
Hurdles on the path to mainstream use
Despite the promise, several challenges must be addressed:
Standardization: Harmonized protocols for exosome isolation, cargo loading, and potency testing are essential to ensure reproducibility across clinics
Scalability: Current ultracentrifuge-dependent production methods are difficult to scale for widespread therapeutic use
Regulatory clarity: Guidelines for regenerative exosome therapies are emerging but not yet well defined, slowing clinical translation
Source optimization: Researchers are still determining the best cell sources for different regenerative applications, such as MSCs versus tissue-specific cells
Companies to watch
The most advanced companies in exosomes for regenerative medicine are distinguished by their clinical progress, manufacturing capabilities, strategic partnerships, and commercial achievements:
Evox Therapeutics: Evox is widely recognized as a leader in the field, pioneering engineered exosome platforms for systemic drug delivery, including complex RNA, gene-editing, and protein therapies. Its DeliverEX platform has enabled partnerships with major pharmaceutical companies and advanced programs targeting hard-to-reach tissues like the brain.
Capricor Therapeutics: This clinical-stage biotechnology company focuses on exosome therapies for severe and rare disorders, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy and cardiac conditions. Capricor’s exosome programs have reached early Phase 1 clinical development, positioning it among the leaders in translating exosome science into human trials.
Aegle Therapeutics: Aegle is advancing AGLE-102, an MSC-derived exosome therapy in human clinical trials for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, a rare skin disorder. Its focus on regenerative and immunomodulatory applications makes it a significant player in the field.
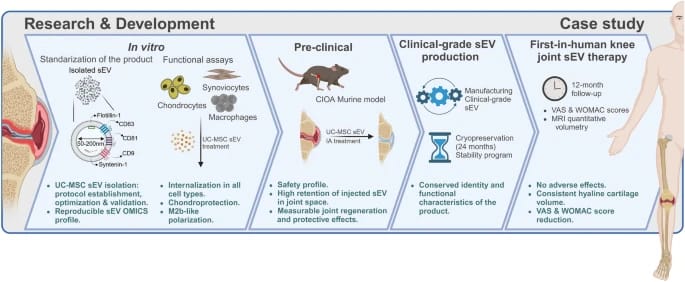
EVast Bio: EVast Bio achieved a milestone with the world’s first human small extracellular vesicle (sEV) therapy application for knee osteoarthritis.
“EVA-100 could revolutionize osteoarthritis treatment, offering a transformative solution for millions if preclinical results are confirmed in both safety and efficacy clinical trials. Our approach aims to go beyond symptom relief by exploring the potential for cartilage regeneration, a key differentiator from existing therapies,” commented Matías Vial, Co-founder & CEO of EVast Bio.
From beauty trend to clinical game changer
While hyped as a secret ingredient in luxury skincare treatments, exosomes are proving to be far more than a cosmetic trend. Their true promise lies in helping patients heal faster, regenerate tissue more effectively, and restore function in ways that traditional medicine has long struggled to achieve.
As we better understand these naturally occurring vesicles, researchers and clinicians are working to bridge the gap between promising lab results and approved therapies that could benefit patients with otherwise difficult-to-treat conditions.
Innovation highlights
🧠 ALZ-protective blood mutation. Researchers discovered that people with TET2 gene mutations in their blood stem cells have a 47% reduced risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer's disease. The mutated immune cells migrate more effectively to the brain and clear harmful amyloid plaques better than normal cells, suggesting a potential protective mechanism against neurodegeneration.
🥽 VR-tually effective. Virtual reality therapy is proving highly effective for treating psychosis, working faster than traditional cognitive behavioral therapy while being equally successful. Patients practice challenging social situations—like shopping or taking buses—in safe virtual environments to overcome paranoid fears and anxiety. The treatment requires 15% fewer sessions and helps people recover sooner, with researchers now exploring AI automation to make it even more accessible.
🦟 Baby steps against malaria. The first malaria treatment specifically designed for babies and very young children has been approved and will roll out in African countries within weeks. Until now, babies weighing less than 4.5kg had no approved malaria drugs, creating a dangerous "treatment gap" where they received adult formulations risking overdose. This is crucial progress since malaria killed 597,000 people in 2023 - almost all in Africa, with three-quarters being children under five. Novartis developed "Coartem Baby" in collaboration with Medicines for Malaria Venture and eight African nations, planning not-for-profit distribution.
🏋️♂️ Sweat your style. Researchers found that matching exercise to personality types makes workouts more enjoyable and effective. Extraverts thrive in high-intensity group activities, while neurotic individuals prefer private sessions with short breaks. People high in conscientiousness exercise regardless of enjoyment, driven by discipline. The study showed neurotic participants experienced the biggest stress reduction, suggesting personalized fitness approaches could help more people stick with exercise routines.
Cool tool
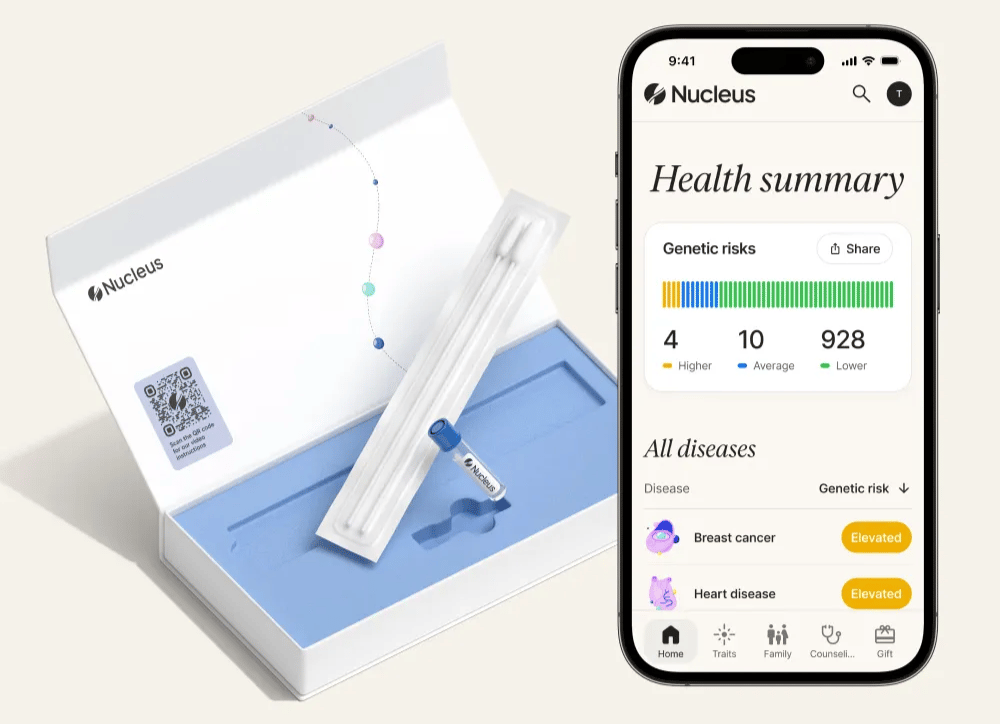
🧬 mynucleus.com takes genetic testing beyond ancestry charts to deliver genuinely actionable health insights. Unlike basic DNA tests that analyze fragments, Nucleus sequences your entire genome (6 billion DNA bases) with 99.9% accuracy, providing risk scores for over 900 health conditions - from cancer and heart disease to mental health disorders and neurological conditions. Optional genetic counseling is available through their SteadyMD partnership.
What sets it apart is the personalization: the app doesn't just look at your genes, but combines them with your lifestyle factors like activity level, smoking habits, and BMI to generate truly individualized risk assessments.
The real value comes from continuous updates - as genetic research advances, your health reports automatically improve. While the 4-6 week wait for results requires patience, the comprehensive insights could make it worthwhile for anyone serious about preventive health planning.
Weird and wonderful
😸 Purr-fect positioning. Scientists analyzed 408 cat videos and discovered two-thirds of cats prefer sleeping on their left side. This isn't random - it's a survival strategy that evolved over millions of years. When cats wake up on their left side, their left visual field connects directly to the right brain hemisphere, which specializes in threat detection, spatial awareness, and escape responses. This positioning helps cats react faster to predators or prey upon waking.
Since cats sleep 12-16 hours daily and are vulnerable during rest, this left-side preference may be an evolutionary adaptation that maximizes their survival chances by optimizing brain processing for quick threat assessment.
Thank you for reading the Healthy Innovations newsletter!
Keep an eye out for next week’s issue, where I will highlight the healthcare innovations you need to know about.
Have a great week!
Alison ✨
P.S. Join over 550 healthcare leaders who get these insights delivered straight to their inbox! Healthy Innovations is read weekly by executives from AstraZeneca, GSK, Vertex, Roche, and leading healthcare startups, agencies, and investors. Subscribe now to stay ahead of industry trends!